EBI: Echtzeit Bauteil Inventarisierung
Real-time scanning and cataloguing of building components in existing structures.
Overview
Period: Nov 2024 – Present
Role: Research Assistant, BTU Cottbus-Senftenberg
Context: Research Project funded by Zukunft Bau (BBR)
Highlights
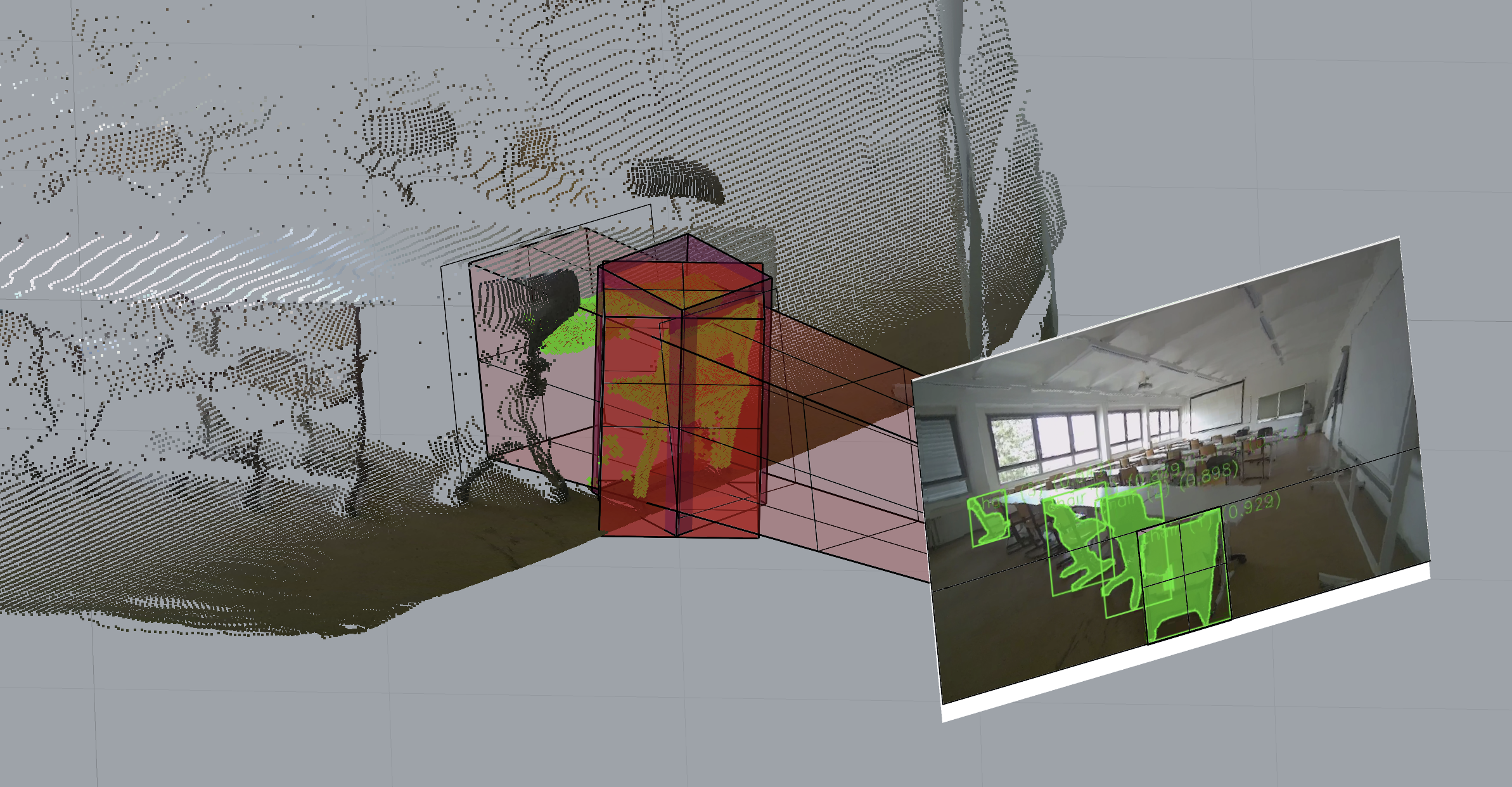
- Orchestrated a perception stack that fuses RGB-D scans with machine vision models for building component detection and counting.
- ...
- ...
Learn more
In-Depth
Reusing components and materials from buildings that are deconstructed provides a promising way of decreasing the footprint of new buildings and increasing the material efficiency within the construction sector. But with the tremendous amount of existing buildings without proper digital representation of containing materials, how can we efficiently make use of these resources?
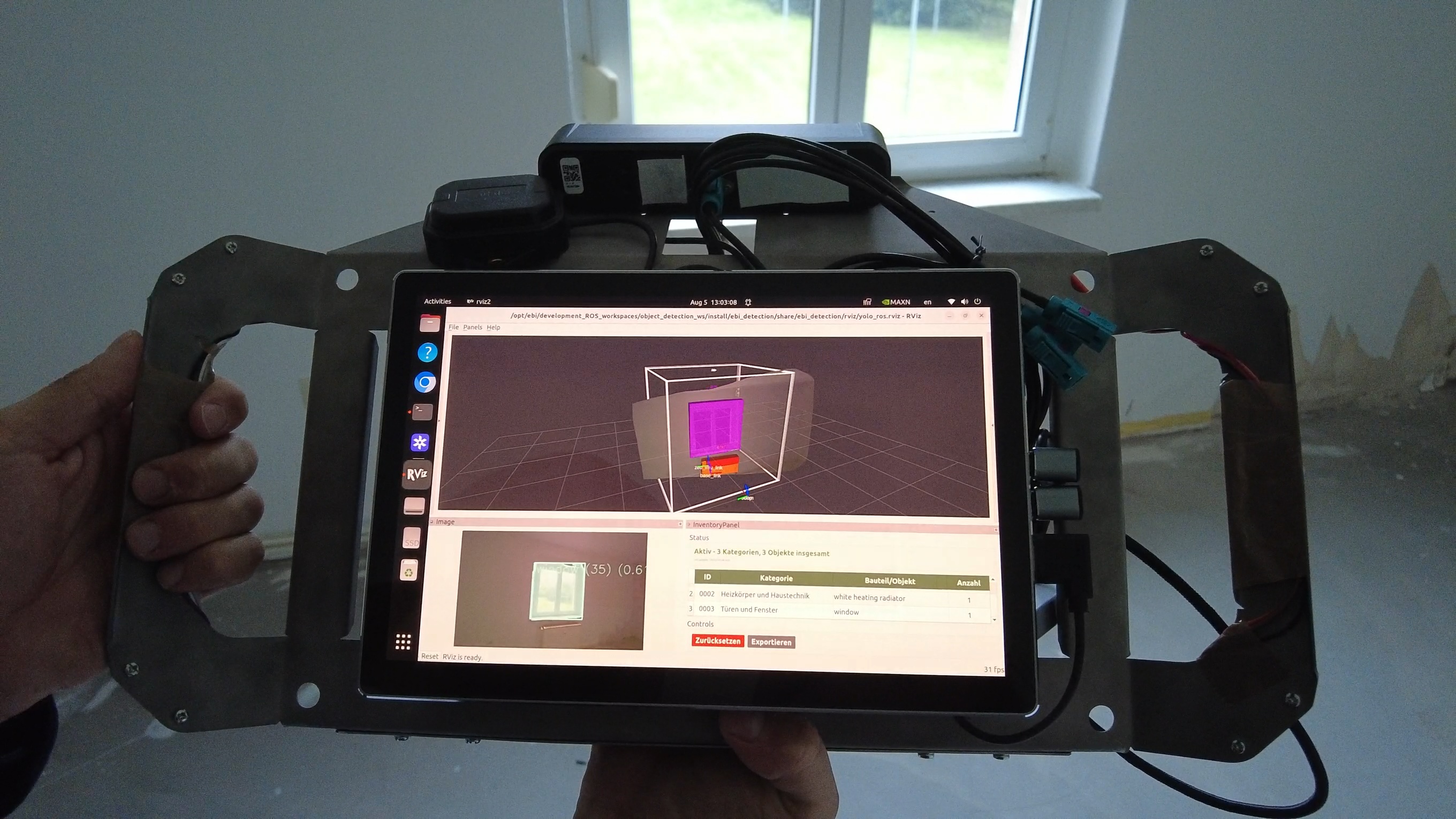
Objective of the EBI project is the development of a real-time system for automated inventory creation of existing buildings. It involves creating hand-held hardware prototypes with edge-AI-inference capable compute and localization sensors (stereo camera, IMUs and GNSS) and pairing these with a real-time software stack building on machine learning models.
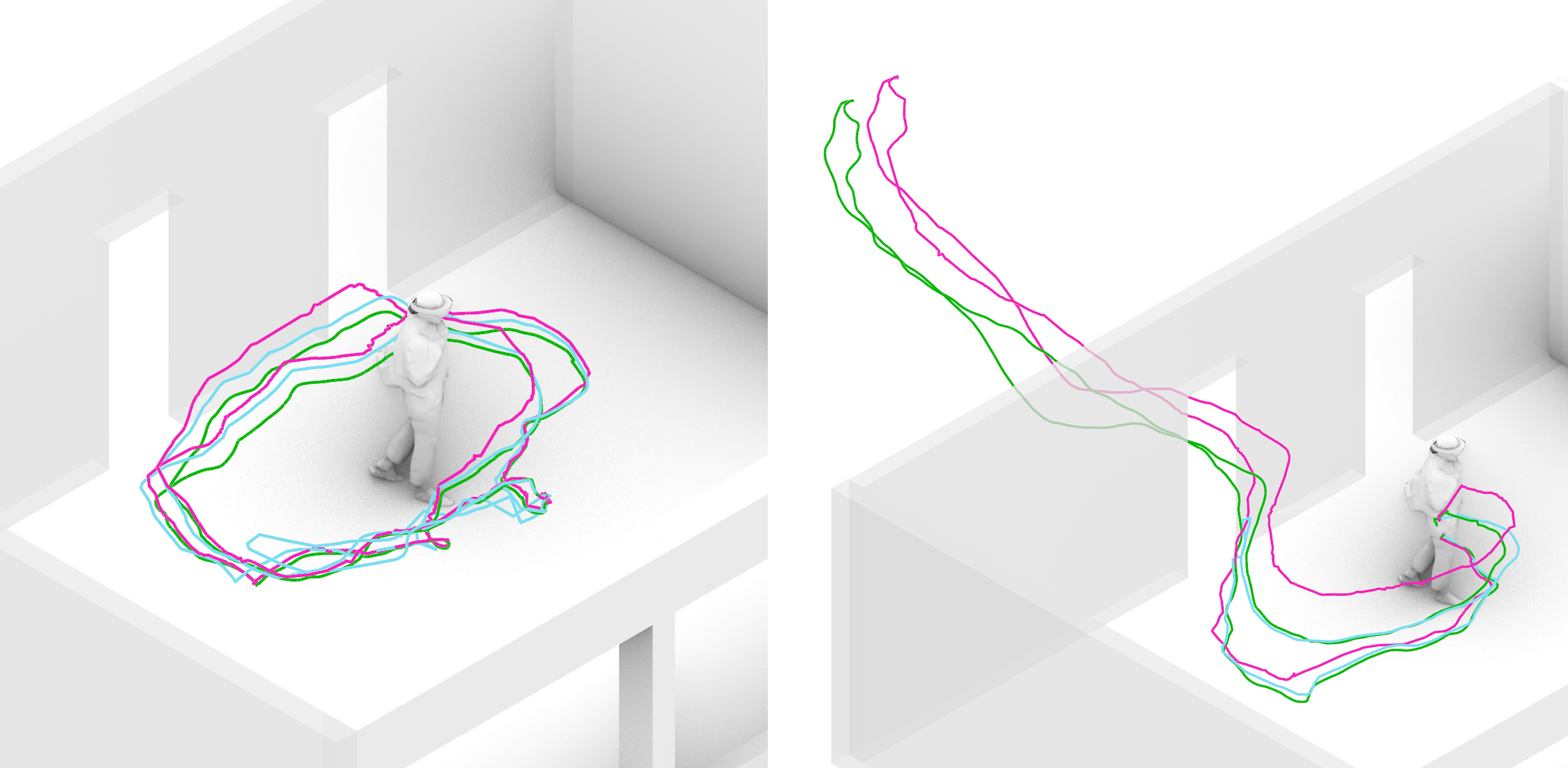
During an on-site building survey, a localization module will provide precise inside-out tracking and spatial position without any prevoius knowledge of the building. Building components are identified image-based and transformed into a spatial representation, continously filling a digital inventory.
As a result a digital inventory consisting of type and amount of building components used in the given building is created. As a data source for material exchange platforms this can lay the groundwork for future use of the materials.
As part of the project a case study in a residential building in Cottbus, Germany is conducted. The building is about to undergo extensive renovation but beforehand, existing building components (windows, doors, heating radiators among others) will be inventorized, both manually as well as with the proposed system and serve as an evaluation of the developed method.
Technologies
ROS, Visiual-inertial Odometry, Convolutional neural networks, Vision language models